RFID Tag for for Warehouse & Logistics Management

Why RFID Tag for for Warehouse & Logistics Management
RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) tags are widely used in warehouse and logistics management for several reasons, primarily due to their ability to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and visibility within the supply chain
Applications in Warehouse management
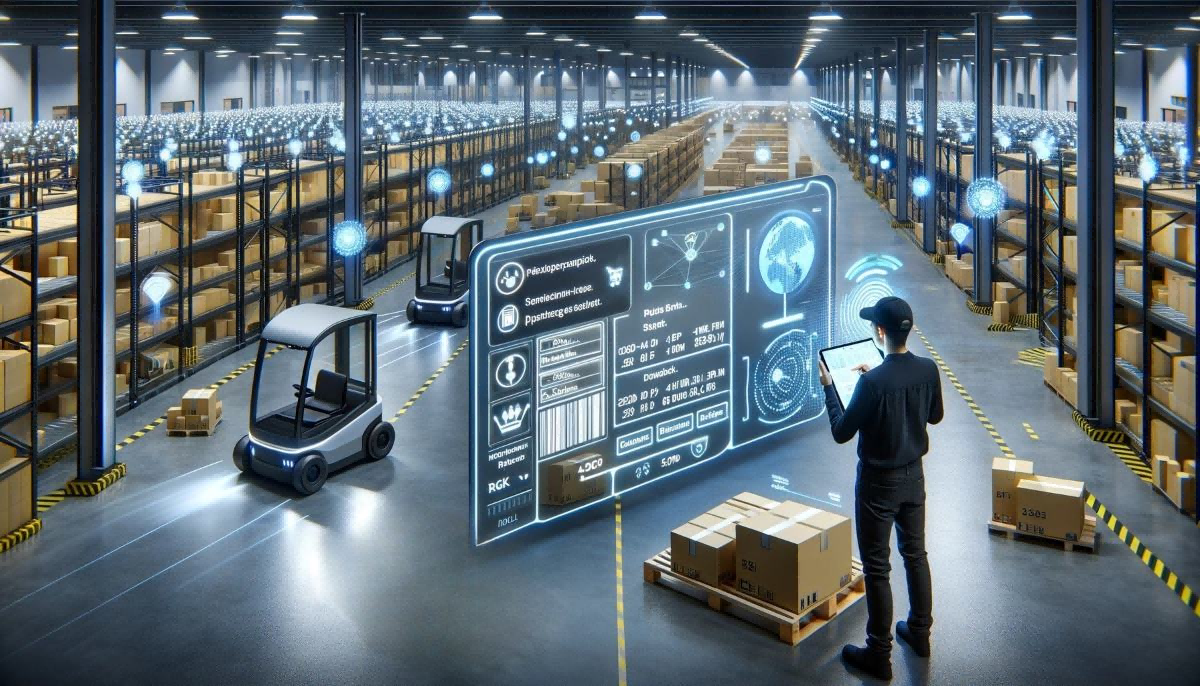
The workflow of an RFID-based intelligent warehouse management system is as follows:

Inbound Process
Staff enter the inbound data into the Warehouse Management System (WMS), associating the goods information with the pallet and deciding whether to assign a specific storage location.
The forklift operator, following the system's instructions, transports the palletized goods to the designated location.
The RFID reading system compares the actual placement position with the system information. If correct, it confirms the completion of the inbound process; otherwise, it prompts the driver to move to the correct location.
When no specific location is assigned, the operator can choose an appropriate spot, and after shelving, the system automatically associates the tag and uploads the information to the backend.

Outbound Process
During the outbound operation, staff issue an outbound command through the WMS, and the forklift receives the task and executes it.
As the forklift picks up the pallet, the RFID reading system retrieves the goods information via the pallet tag. If the information matches what is specified in the WMS, the goods are allowed to be dispatched; otherwise, an alarm is triggered.
The outbound process is essentially the reverse of the inbound process.

Transfer Within Warehouse
- Transfer within the warehouse involves an internal outbound and inbound process, adhering to the same control principles as the regular inbound and outbound processes.
- The application of RFID technology optimizes these processes, improving work efficiency, ensuring smooth production, reducing labor and labor intensity, enabling real-time inventory management, lowering operational costs, and significantly enhancing economic benefits.

Hardware Composition:
- RFID equipment must have dust-proof, water-resistant, and shock-resistant features, as well as the ability to withstand voltage and current fluctuations. The casing needs to be robust, durable, corrosion-resistant, and have good temperature adaptability.
- The ARU UHFRFID is a vehicle-grade ultra-high frequency RFID reader that complies with the automotive industry standard TS16949 and meets Industry 4.0 requirements, making it suitable for forklift and automotive applications.
- For RFID antennas, a Wide Range Antenna can be selected, offering precise read ranges of 30 degrees and 70 degrees.











