NFC Tag Solution
Why NFC Tag has different application?
NFC (Near Field Communication) is widely used due to its key advantages:
Convenience: Users can easily tap or bring their device close to an NFC tag or reader for quick data transfer, payments, or identification, making it ideal for fast interactions.
Short-Range Communication and High Security: With a typical range of 10 cm or less, NFC is more secure than other wireless technologies, making it suitable for mobile payments and identity verification.
Fast Connectivity and Response: NFC connects almost instantly, typically within 1/10th of a second, eliminating the need for pairing, ideal for immediate feedback applications.
Versatility: NFC supports both active and passive modes, allowing a wide range of applications from payments to data sharing.
Application and picture
Mobile Payments
Examples: Apple Pay, Google Pay, Samsung Pay
Users can make secure, contactless payments by tapping their smartphone or smartwatch on an NFC-enabled payment terminal. This offers a faster and more convenient alternative to traditional payment method。
Access Control and Identification
Examples: Office entry systems, hotel room keys, event passes
NFC is used for secure access control and identification. Users can simply tap their NFC card or smartphone against the reader to gain access quickly and conveniently.

Transportation and Ticketing
Examples: Public transit cards, subway tickets, e-tickets
NFC technology replaces traditional transit cards, allowing users to pay for fares by tapping their phone or NFC card against a reader, improving the overall convenience of public transportation.

Information Sharing and Marketing
Examples: Smart posters, product packaging, advertisements
NFC tags can store website links, product information, or promotional offers. Consumers can tap their phones on the NFC tag to access relevant information, enhancing their engagement with the product or brand.

Device Pairing
Examples: Bluetooth speakers, headphones, printers
NFC enables quick pairing of devices such as Bluetooth speakers or headphones. Users can connect their devices by simply tapping them together, eliminating the need for a lengthy pairing process.

Smart Home Control
Examples: Controlling lights, thermostats, sound systems
Users can set up NFC tags as control switches for smart home devices. By tapping their phones on the tag, they can activate or adjust various smart home functions, making everyday life more convenient.

Healthcare and Medical Applications
Examples: Electronic medical records, medication tracking
NFC technology allows medical staff to quickly access patient records by scanning an NFC tag, ensuring accurate treatment. It can also verify the authenticity of medications, reducing the risk of counterfeit drugs.

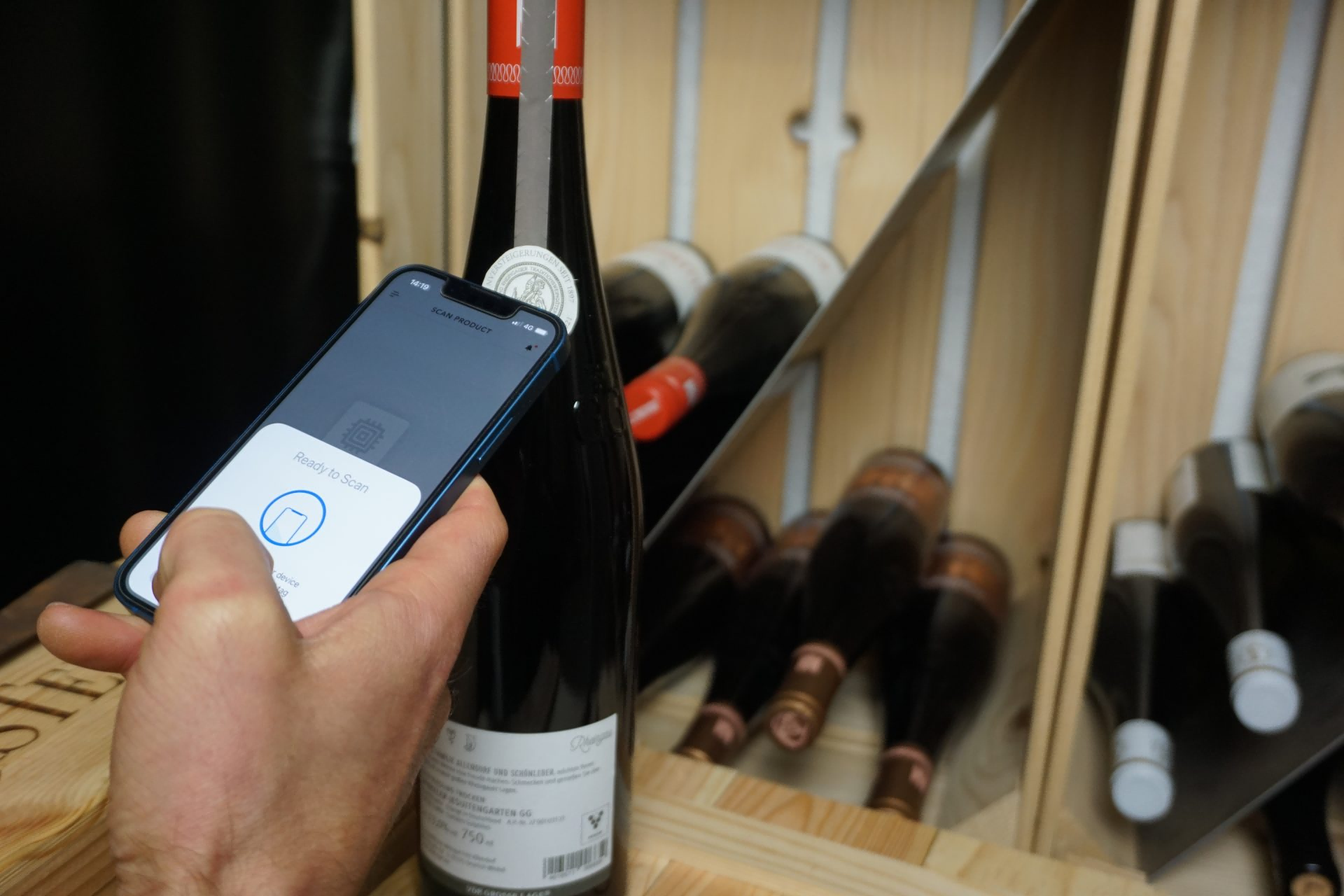
Anti-Counterfeiting Identification
Examples: High-end products, luxury goods, pharmaceuticals
NFC technology can be embedded into products to provide a unique identifier. Consumers can use their smartphones to verify the authenticity of the product by scanning the NFC tag, helping to protect against counterfeit goods and ensuring brand integrity.

Recommended article
No data available






